Operations Department: SOPs, Compliance, Vendor Coordination & Process Governance
In every successful business, the operations department plays a vital role as the backbone of organizational effectiveness. Unlike production, which focuses on creating goods, or R&D, which emphasizes innovation, operations ensures that all functions work together seamlessly. From defining Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to ensuring compliance, coordinating with vendors, and governing processes, the operations team provides the framework for efficiency, stability, and growth.
This blog explores four essential pillars of the operations department: SOPs, compliance, vendor coordination, and process governance. Each of these elements contributes to operational resilience, reducing risks, and ensuring that organizations stay agile in a competitive business environment.
The Role of the Operations Department
The operations department is often referred to as the “nervous system” of an organization. It ensures that internal and external workflows align with company goals. Some of its major responsibilities include:
- Defining SOPs – Establishing documented guidelines for consistency.
- Ensuring Compliance – Meeting legal, regulatory, and industry standards.
- Vendor Coordination – Building and maintaining efficient supplier partnerships.
- Process Governance – Monitoring, auditing, and improving business processes.
- Resource Optimization – Balancing people, technology, and capital effectively.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs are detailed, step-by-step instructions designed to ensure consistency and quality in business processes. They act as the organizational playbook, enabling employees to follow structured guidelines regardless of department or role.
Importance of SOPs:
- Consistency – Ensures uniform results across teams and locations.
- Training Tool – Speeds up onboarding for new employees.
- Error Reduction – Reduces ambiguity in tasks, minimizing mistakes.
- Scalability – Facilitates smooth expansion across markets.
Challenges with SOPs:
- Keeping documentation updated in fast-changing industries.
- Employee resistance to following structured methods.
- Over-standardization, which may reduce flexibility.
Best Practices:
- Review and update SOPs annually or whenever processes change.
- Involve employees in SOP creation to improve adoption.
- Leverage digital tools for easy access and version control.
Example: In the food and beverage industry, SOPs govern hygiene, storage, and preparation methods. A well-defined SOP ensures that every branch of a restaurant chain delivers the same taste, quality, and customer experience.
Compliance: Meeting Legal and Regulatory Standards
Compliance refers to adhering to laws, regulations, and ethical standards relevant to the business. From labor laws and safety standards to industry-specific regulations, compliance ensures organizations avoid risks such as penalties, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
Why Compliance Matters:
- Legal Protection – Reduces the risk of fines and legal action.
- Brand Reputation – Shows commitment to ethical and lawful conduct.
- Operational Continuity – Prevents disruptions due to regulatory violations.
- Investor Confidence – Builds trust with stakeholders and partners.
Types of Compliance:
- Regulatory Compliance – Government rules (e.g., labor, taxation, environment).
- Industry Standards – Certifications like ISO, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
- Internal Compliance – Company policies, ethics, and codes of conduct.
Example: A pharmaceutical company must adhere to FDA or equivalent regulations. Non-compliance not only leads to heavy fines but can also endanger lives and permanently damage brand credibility.
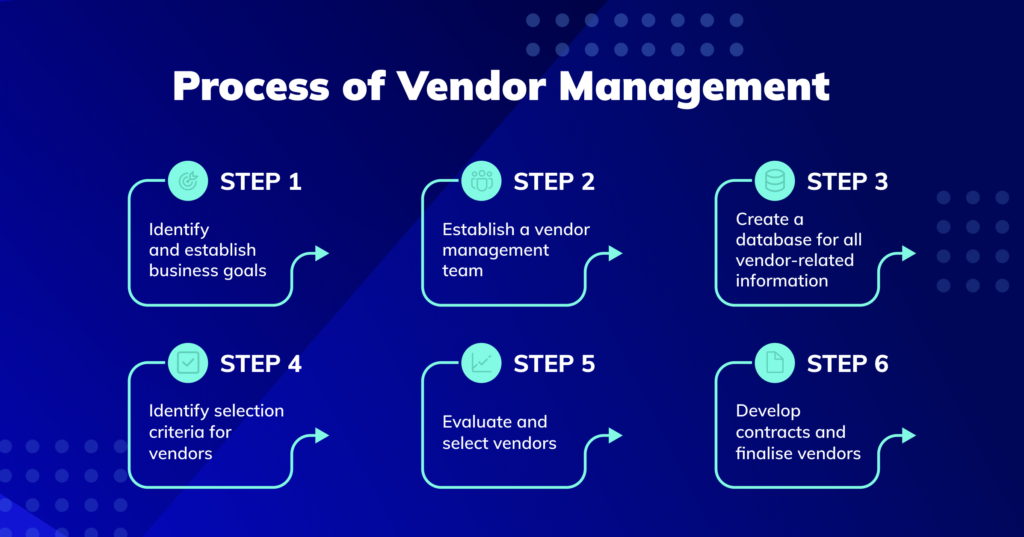
Vendor Coordination: Building Efficient Partnerships
Vendors and suppliers are critical to operational success. Smooth vendor coordination ensures the timely flow of raw materials, services, and support, directly impacting productivity and customer satisfaction.
Importance of Vendor Coordination:
- Reliability – Prevents delays in supply chains.
- Cost Efficiency – Better negotiation reduces expenses.
- Quality Assurance – Reliable vendors improve product and service standards.
- Risk Reduction – Diversified vendor networks prevent dependence on a single source.
Challenges:
- Managing multiple vendors across geographies.
- Ensuring transparency in pricing and contracts.
- Balancing long-term relationships with competitive sourcing.
Best Practices:
- Use Vendor Management Systems (VMS) for contracts and performance tracking.
- Establish clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with measurable KPIs.
- Maintain regular communication and performance reviews.
Example: In retail, efficient vendor coordination ensures shelves remain stocked. If a supplier fails, operations suffer, leading to empty shelves and disappointed customers.
Process Governance: Monitoring and Improving Efficiency
Process governance refers to establishing clear accountability, measurement, and continuous improvement of business workflows. It ensures that company processes align with strategic goals and deliver maximum efficiency.
Why Process Governance Matters:
- Transparency – Clarifies roles, responsibilities, and decision-making.
- Risk Management – Identifies and addresses inefficiencies before they escalate.
- Performance Measurement – Provides benchmarks for improvement.
- Strategic Alignment – Ensures daily operations support long-term goals.
Techniques in Process Governance:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) – Measuring output, costs, and quality.
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR) – Redesigning workflows for efficiency.
- Lean and Six Sigma – Continuous improvement methodologies.
- Internal Audits – Monitoring compliance with SOPs and regulations.
Example: A logistics company implementing process governance may track delivery times, fuel consumption, and customer feedback to identify inefficiencies and implement corrective actions.
Integration: How SOPs, Compliance, Vendor Coordination, and Governance Work Together
Each of these pillars strengthens the others. SOPs provide structured workflows, which support compliance. Compliance reduces risks and ensures credibility with vendors. Vendor coordination ensures reliable inputs for processes. Process governance ties everything together by monitoring and refining systems. Collectively, they create a resilient operational ecosystem.
Challenges Facing Modern Operations Departments
- Globalization – Managing compliance and vendors across borders.
- Technological Change – Adapting SOPs and processes to digital tools.
- Supply Chain Risks – Political instability, pandemics, and climate change impact vendors.
- Employee Training – Ensuring staff are aligned with SOPs and compliance needs.
Future Trends in Operations Management
- AI-Driven Compliance Monitoring – Automated checks for legal and regulatory adherence.
- Blockchain for Vendor Coordination – Transparent, tamper-proof contracts.
- Digital SOPs – Cloud-based, interactive playbooks.
- Process Automation – Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for repetitive workflows.
- Sustainability Integration – Green operations and ethical vendor selection.
Conclusion
The operations department is the cornerstone of organizational stability. By focusing on SOPs, compliance, vendor coordination, and process governance, businesses can establish a resilient and efficient framework. These pillars ensure that day-to-day tasks align with long-term strategy, reduce risks, and enhance competitiveness.
In today’s dynamic environment, operations excellence is no longer a back-office function but a strategic differentiator. Organizations that master operational discipline will not only achieve efficiency but also build trust, resilience, and long-term success.